Describe the Structure of Alkanes and Their Different Uses
Alkanes are used as good lubricants and preservatives for the metals because they protect the metal surface from reaching water. Alkanes having 1-4 carbon atoms are gases then from 5-17 carbon atoms they are liquid and alkanes having 18 or more carbon atoms are solid at 298K.
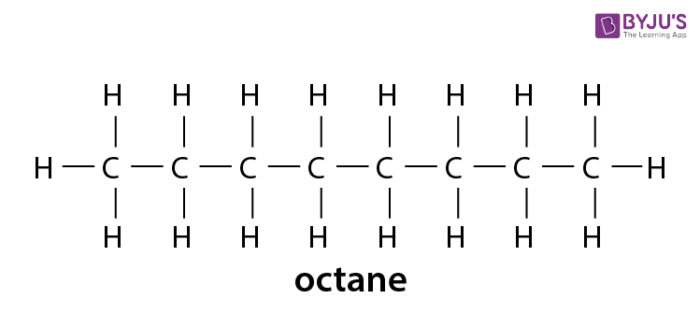
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons.

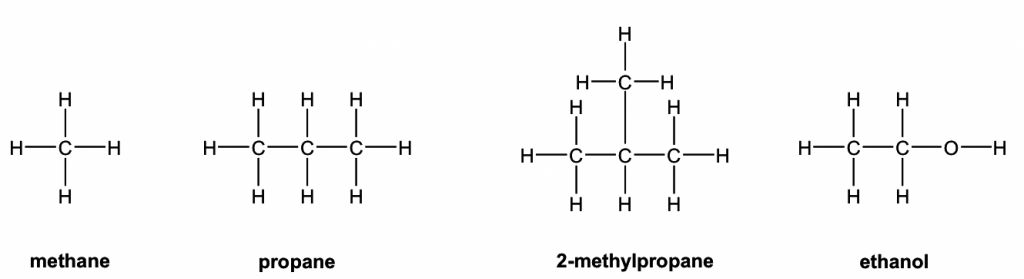
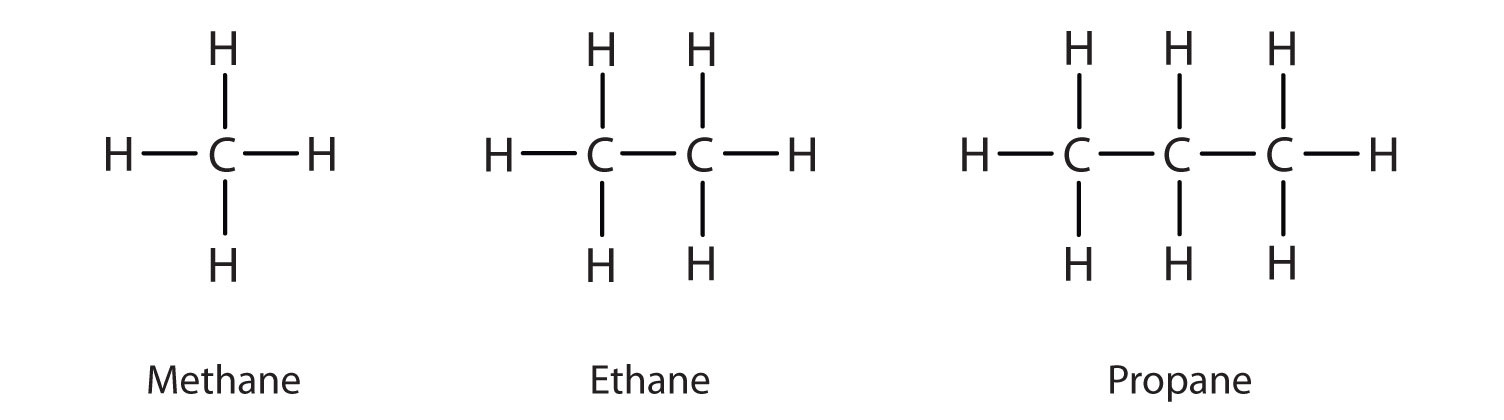
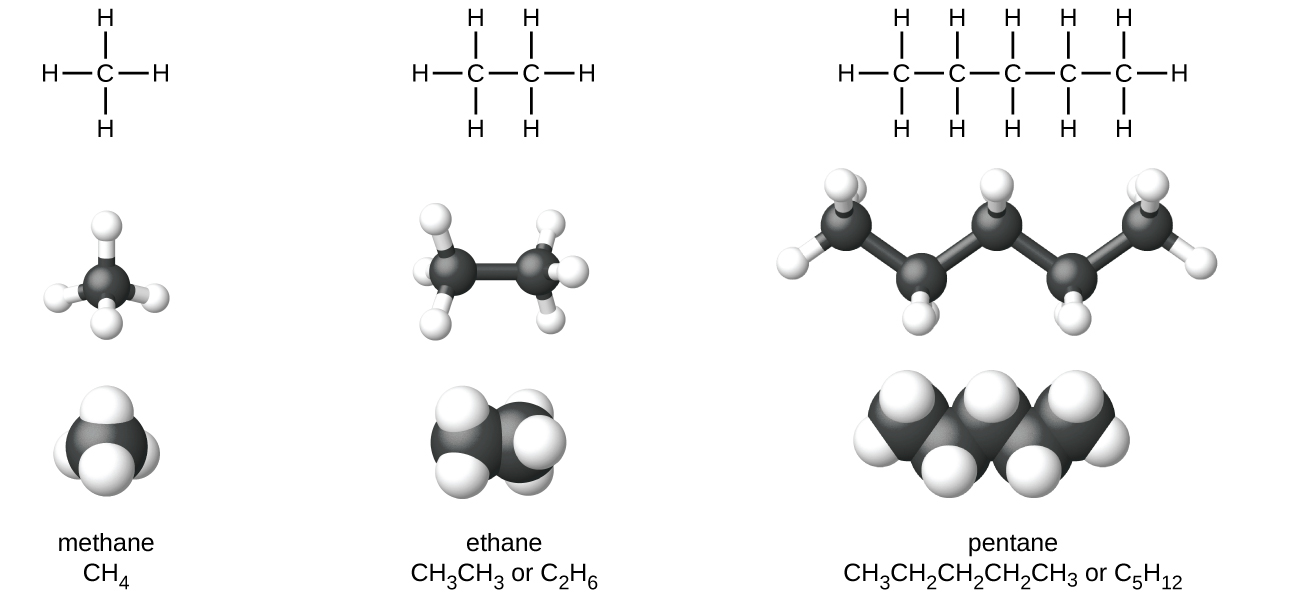
. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons which can be used as fuels lubricants and as starting materials for a wide range of other compounds. Alkanes also known as paraffins or saturated hydrocarbon are chemical compounds that consist only of the element carbon c and Hydrogen H ie hydrocarbons wherein these atoms are linked together exclusively by. Structures of Alkanes 21A Organic chemists use a variety of different types of structures to represent alkanes such as these shown for methane one C ethane two Cs and propane three Cs.
- one bond is a sigma bond. Structure of alkanes - In alkanes all the carbon atoms are sp³ hybridised which means that they form four sigma bonds with either carbon or hydrogen. This is a type of alkane with a single carbon bond and has the chemical formula of CH4.
Alkanes are the typical oils used in many non-polar solvents and they do not mix with water. These alkanes have different uses as we are going to discuss below. They comprise only hydrogen and carbon.
Vapours rise up the column and cool condensing when they meet their boiling point. Alkanes Alkanes are generally unreactive. Their structure is defined by a reactive carbon-carbon double bond they have a general formula of CnH2n they can be named by following a series of simple steps they have many uses in nature as well as in industrial and laboratory settings and some of their most common reactions include hydrogenation alkene to alkane halogenation alkene to.
Short chain alkanes are collected near the top as they have lower boiling points. The most simple alkane is methane with the formula CH 4. These are cylindrical in shape and are very strong - the other is a pi π bond.
1 Structure of Alkenes Alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes have one or more double bonds The two bonds in a double bond are different. For instance methane represents one carbon atom propane represents three heptane represents seven and decane represents ten. Give a use of alkanes.
Without consulting tables arrange the following alkenes in order of increasing boiling point. Physical Properties of Alkanes and Their Variations. From the previous discussion of formula analysis the formulas for such hydrocarbons will be C n H 2n22r where n is the number of carbon atoms and r is the number of rings.
Crude oil is heated to a vapour which passes into the column. Alkenes have physical properties low boiling points insoluble in water quite similar to those of their corresponding. This group of compounds consists of carbon and hydrogen atoms with single covalent bonds.
For example if we mix an Alkane with water. Alkanes which have long carbon chains are often called paraffins in chemical industry. Alkanes from 17 carbon upwards form the most important components ofFuel oil and lubricating oilalso used as anti-corrosive agents as their hydrophobic nature means that water cannot reach the metal surface.
Alkanes contain only CH and CC bonds which are relatively strong and difficult to break. This makes them relatively unreactive apart from their reaction with oxygen in. Alkanes are a series of compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen atoms with single covalent bonds.
Petroleum is a mixture of alkanes with different chain lengths which are separated in a process called fractional distillation. These are known as saturated hydrocarbons. How do these properties compare to those of the alkanes.
These involve sideways overlap of p-orbitals and are weaker than bonds Alkenes are flat and. In organic chemistry an alkane or paraffin a historical trivial name that also has other meanings is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. Graphic 21 Kekulé Electron-Dot and Three-Dimensional Structures.
The similar electronegativities of carbon and hydrogen give molecules which are non-polar. The column is hotter at the bottom and cooler at the top. The structure and names of the ALKENE hydrocarbons unsaturated Alkenes are a family of hydrocarbons containing at least one covalent carboncarbon double bond CC.
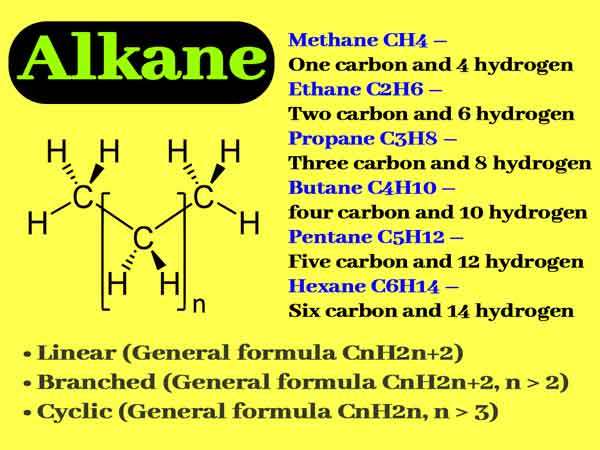
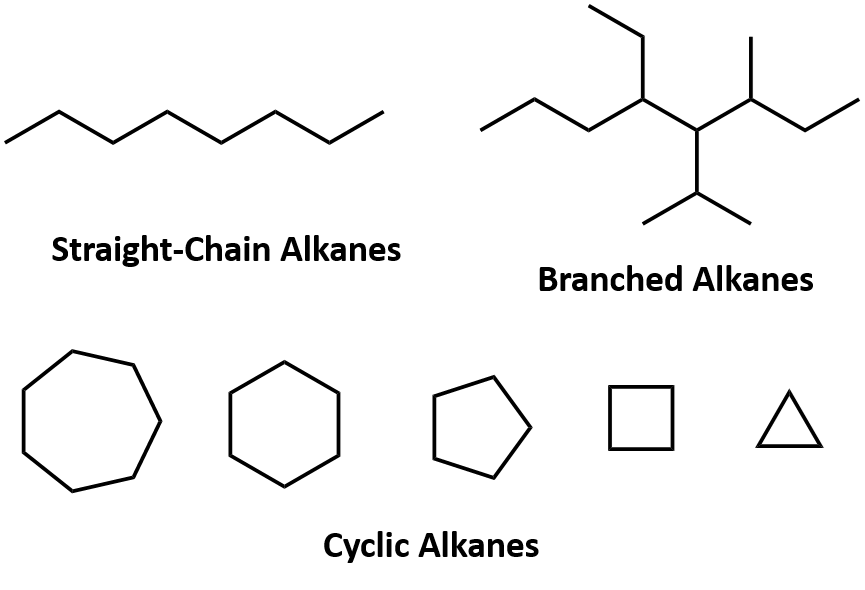
Chain alkanes cycloalkanes and branched alkanes. Alkanes are organic compounds composed of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms. The general formula of alkanes is C n H 2n2.
Briefly describe the physical properties of alkenes. Alkanes with 35 or more carbon atoms are used for road surfacing. Such compounds are necessarily hydrocarbons made up of chains and rings of carbon atoms bonded to a full complement of hydrogen atoms all carbons are sp 3 hybridized.
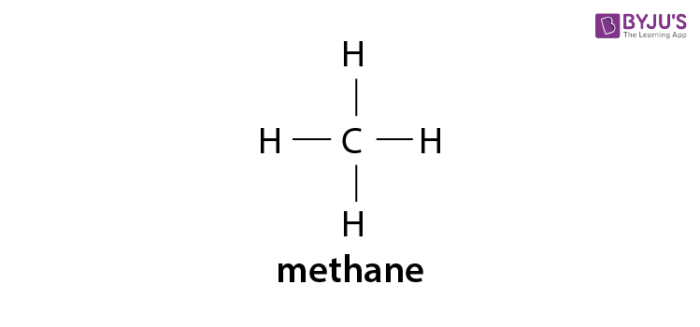
The formula for alkanes is CnH2n2. The structures showing C and H atoms connected by lines are Kekulé structures. The second alkane is ethane with the formula C 2 H 6.
The main source of alkanes is petroleum. The first four alkanes are methane CH 4 ethane C 2 H 6 propane C 3 H 8 and butane C 4 H 10. Alkanes have the general chemical formula CnH2n2.
The most basic family of compounds has been called alkanes. The CC double bond is called the functional group of the homologous series we call alkenes. The densities of Alkanes are lower than the density of water.
Also comprises a homologous series having a molecular formula of CnH2n2. Their density value is nearly 07 g mL-1 considering the density of water as 10 g mL-1. They can be categorized into three groups which are.
This means that their carbon atoms are joined to each other by single bonds. Structural Isomers the atoms in each molecule are connected in a different order. Many solid alkanes find use as paraffin wax also.
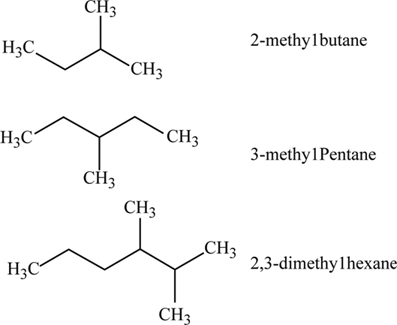
C2H6O H C H H C H H OH OCCH H H H H H Ethyl Alcohol Dimethyl Ether Colorless liquid mp -117C bp 785C density 0789 gmL. Alkanes are the simplest family of. Chapter 1 Alkanes 13 25 Isomers Isomers compounds having identical molecular formulas but different arrangements of atoms.
In other words an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carboncarbon bonds are single. Compounds containing alkynes carbon-carbon triple bonds like ethinyl estradiol and norethynodrel in their chemical structure are used in the pharmaceutical industry as oral contraceptives.
What Is The Bonding Structure Of Alkanes Quora
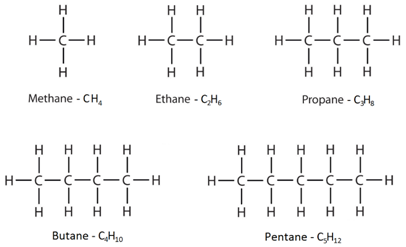
4 21 Understand How To Draw The Structural And Displayed Formulae For Alkanes With Up To Five Carbon Atoms In The Molecule And To Name The Unbranched Chain Isomers Tutormyself Chemistry

Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry
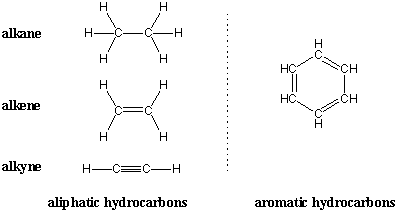
File Alkane Structure 1 Gif Wikimedia Commons

Alkanes Formula Types Nomenclature Structure Properties Uses

The Molecular Structure Of The First Four Alkanes 8 Download Scientific Diagram
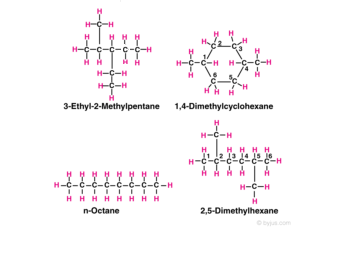
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes

Structures And Names Of Alkanes
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes
Chemical Properties Of Alkanes What Are Examples Of Alkanes
Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry
Definition Of Alkanes Chegg Com
2 1 Structures Of Alkenes Organic Chemistry I
Structures And Names Of Alkanes


Comments
Post a Comment